Imagine a hotel – a single building with multiple rooms. Despite being separate and private, all of the rooms share the same physical structure. The same concept maps to “Virtualization”. Virtualization turns one powerful computer into many isolated, efficient environments using smart software. In this blog, we’ll explore what virtualization in cloud computing is, how it powers cloud computing, the different types of virtualization, and the key tools and benefits that make it essential in today’s digital landscape. Let’s explore virtualization world with WeCloudData!
What Is Virtualization?
The process of creating a virtual computing environment that allows multiple operating systems and applications to run on a single computer is known as virtualization. Along with the operating system, virtualization also enables the creation of virtual instances of hardware, storage devices, and network resources. virtualization in cloud computingallows for the full utilization of hardware capabilities by distributing a physical machine’s resources among multiple users.
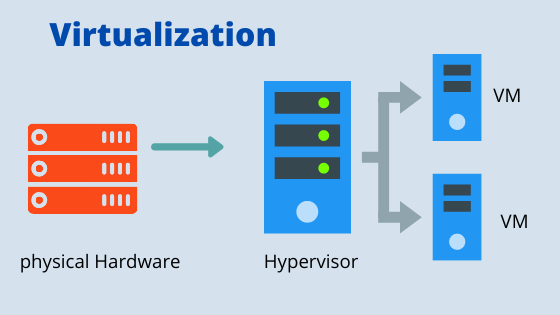
How Does Virtualization Actually Work?
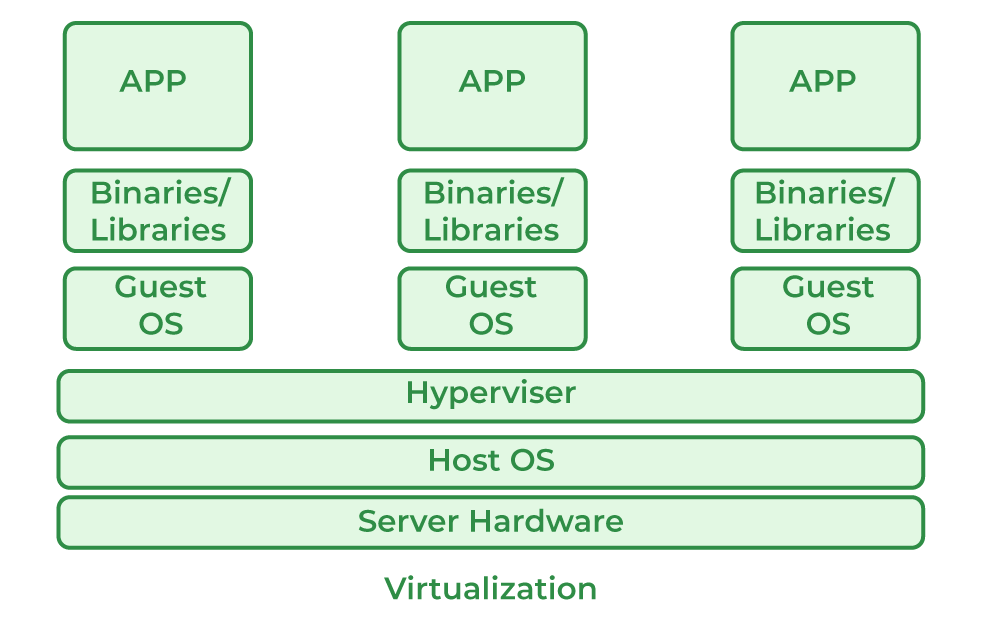
The heart of virtualisation is a software called a hypervisor. Consider the hypervisor as a hotel manager responsible for managing rooms (virtual machines). It keeps the rooms isolated, assigns resources like memory and CPU, and ensures each room operates smoothly. Let’s break down the process of virtualisation step by step.
Hardware Layer
The first layer is the hardware layer. This layer includes physical components like the CPU, memory, storage, and network interfaces.
Hypervisor Layer
The hypervisor acts as a coordinator between virtual machines and the hardware. It is a position as a coordinator layer on top of hardware or within a host OS. The hypervisor provides an interface to the physical environment, ensuring that each virtual machine has access to physical resources.
It is categorised into two main types:
- Type 1 (Bare-metal): Runs directly on physical hardware (used in servers, data centers).
- Type 2 (Hosted): Runs on top of an existing OS (ideal for desktops, development environments).
Virtual Machines
Each Virtual Machine is like a separate guest room. This isolation allows multiple VMS to run independently on a single machine. Each virtual machine contains its own resources, including the operating system, applications, and files. The key properties of VMS are;
● Partitioning
● Isolation
● Encapsulation
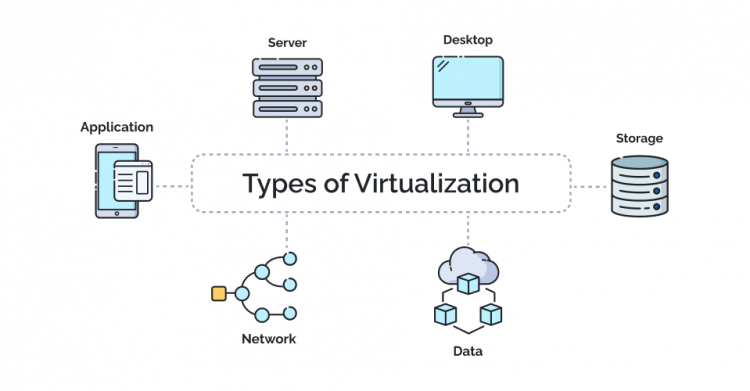
Types of Virtualization
There are multiple types of virtualization. The main type of virtualization is explained briefly below;
1. Server Virtualization
Server virtualization divides a single physical server into multiple virtual servers, increasing server efficiency and simplifying IT operations.
2. Desktop Virtualization
The desktop virtualization creates virtual desktops that users can access remotely. Great for hybrid work and secure enterprise environments.
3. Application Virtualization
Application virtualization allows users to run apps without installing them on their local machines.
4. Storage Virtualization
Storage virtualization pools storage from different devices and presents it as a single resource, making management easier.
5. Network Virtualization
Network virtualization combines network resources, such as routers and switches, into a virtual network that can be easily configured and scaled.
6. Data Virtualization
Data virtualisation provides a unified view of data from multiple sources without requiring it to be moved. It is ideal for analytics and integration.
The Role of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualisation plays a crucial role in cloud computing. It enables cloud service providers to provide effective and scalable services like:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provisioning virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Delivering hardware and software tools over the internet.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Providing software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
By using virtualization in cloud computing, these cloud models offer enhanced scalability, cost-effectiveness, and resource management.
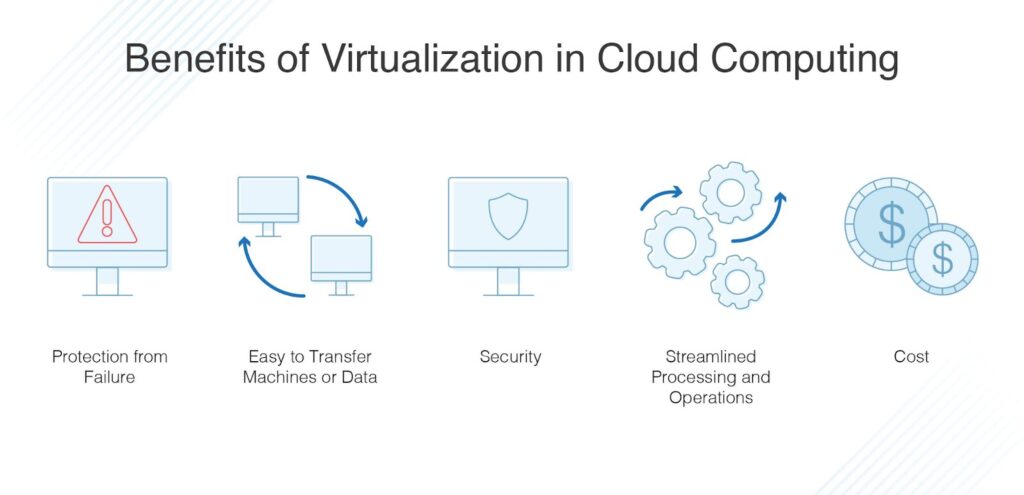
Benefits of Virtualization
Here are the benefits virtualization in cloud computing offers to businesses and developers.
- Efficient Resource Use: One physical server can host many virtual machines, reducing hardware waste.
- Scalability: Spin up or remove VMS as needed – perfect for fluctuating workloads.
- Cost Savings: Less hardware = lower costs for energy, maintenance, and infrastructure.
- Faster Disaster Recovery: VMS can be backed up and restored quickly, which improves business continuity.
- Security & Isolation: Even if one Virtual Machine is compromised, others remain unaffected.
Virtualization Examples
Here are the key examples for virtualization.
- VMware, which specializes in server, desktop, network, and storage virtualization.
- IBM Cloud offers virtual servers and storage that adapt to workload demands.
- Citrix, focuses on application virtualisation but also provides server virtualization and virtual desktop solutions.
- Microsoft, whose Hyper-V virtualisation technology focuses on virtualised desktop and server systems, comes with Windows.
- Google Cloud Compute Engine provides customizable virtual machines that power everything from websites to enterprise apps.
Virtualization: One Computer, Many Worlds
Virtualization in cloud computing is no longer just a trend, it’s the foundation of cloud computing. From IaaS (Google Compute Engine) to SaaS (Office 365), virtualization supports the modern digital world to run smoothly, securely, and efficiently.
Whether you’re managing IT infrastructure or just curious about how cloud apps work, understanding virtualization in cloud computing provides a broad perspective on how technology can accomplish a lot with minimal physical hardware.
Learn with WeCloudData: Upskill Your Team in Cloud & Data Technologies
Looking to empower your team with the latest in cloud computing, data engineering, and AI technologies? WeCloudData’s Corporate Training programs are tailored to meet the needs of forward-thinking companies. With hands-on, expert-led instruction, our courses are designed to bridge the skills gap and help your organization thrive in today’s data-driven economy.
Upskill with WeCloudData: Become a Cloud Engineer & Analytics Leader
Our Cloud Engineer Track delivers a comprehensive, hands-on approach to cloud engineering, equipping you with the skills to design, deploy, and manage secure, scalable, multi-cloud environments. The courses included in the cloud computing learning track include;
- Python Fundamentals
- Introduction to Linux
- Introduction to Docker
- AWS Fundamentals
- Azure Fundamentals
- GCP Fundamentals
Why This Program?
- End-to-End Cloud Mastery: From core principles to advanced architectures across AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Enterprise-Grade Skills: Learn industry best practices for DevOps, resilience, and cost-optimized solutions.
- Real-World Readiness: Apply knowledge through hands-on projects and case studies mirroring modern IT challenges.

