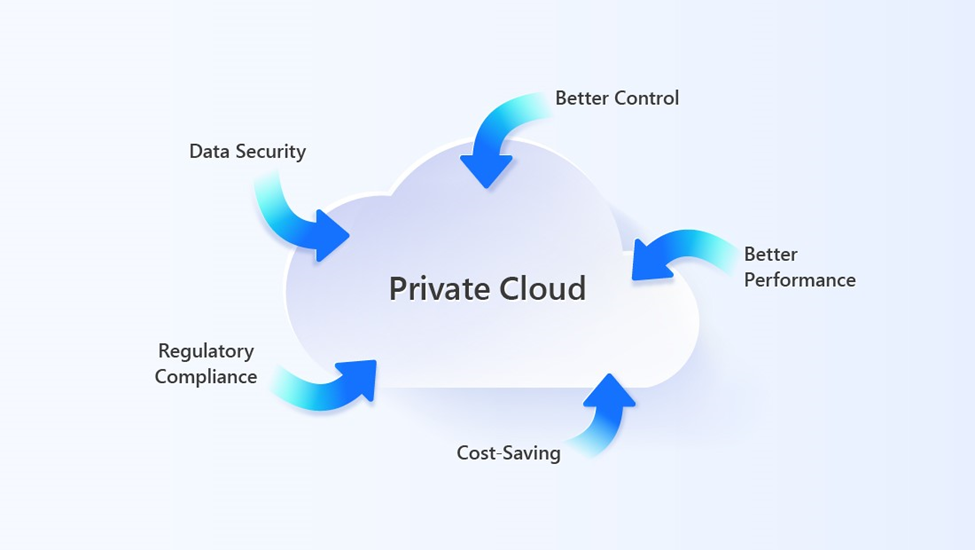
A private or enterprise cloud is the type of cloud computing in which all the resources are dedicated to a single tenant. Private cloud allows organizations a high level of cloud computing benefits such as scalability, flexibility, access control, and faster service delivery.
This blog explores the fundamentals of the private cloud framework. Let’s learn more about Private Cloud with WeCloudData!
What is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a computing model that provides cloud services and infrastructure only to a single organization. A third-party cloud service provider can manage it, or the organization can host it on-site in its own data center. Private clouds provide more security, compliance, and infrastructure control than public clouds because they are not shared with multiple organizations.
Modern private clouds have evolved beyond static virtual machines. They now incorporate features like AI-powered security, container orchestration, and policy-based automation, making them not only secure but also developer-friendly.
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud: Which One Leads in 2025?
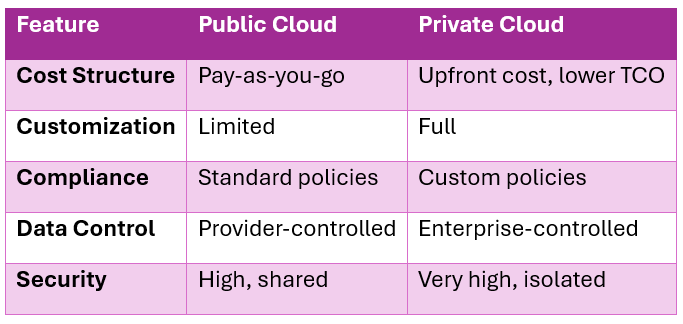
The classic private cloud vs public cloud argument has evolved into an informed choice based on use cases rather than general pros and cons. While public clouds such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer rapid scalability, private clouds deliver exclusive control, customization, and security, especially where sensitive data is involved. Rather than focusing on private cloud vs public cloud debate. Nowadays, organizations are opting for a hybrid solution combining both public and private cloud models, enjoying the benefits of both for different scenarios.
How Private Cloud Works
Private cloud architectures utilize three foundational technologies: virtualization, management software, and automation to maximize resource efficiency.
Virtualization
Virtualization is the foundation of private cloud computing. Businesses use virtualization to maximize their hardware resources and boost their return on investment. Virtualization maximizes hardware usage by enabling several virtual machines to operate on a single physical machine. In this field, platforms such as VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM remain dominant.
Automation
Automation is about intelligent operations, not just resource provisioning. Red Hat Ansible and Terraform are two AI-driven automation tools that incorporate Infrastructure as Code (IaC) principles to reduce human error, speed up deployments, and facilitate CI/CD pipelines. The best example of cloud automation is the automation of server provisioning and integration.
Additionally, private cloud makes use of cutting-edge technologies like containers, microservices, and DevOps. Along with facilitating a seamless move to a public cloud or hybrid cloud environment, these technologies also improve efficiency and flexibility.
Management Software
Cloud service administrators manage infrastructure and services provided by a cloud by using management software. OpenStack, VMware Cloud Foundation, and Nutanix Cloud Platform are examples of intelligent management stacks that are essential to modern private clouds. These solutions offer unified dashboards for policy enforcement, control, and visibility.
Types of Private Cloud
Private cloud isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The deployment model the organization chooses depends on scalability, security, and management requirements.
Private cloud has four main types depending on who controls the private cloud environment;
Virtual private cloud, managed private cloud, hosted private cloud, and on-premise private cloud.
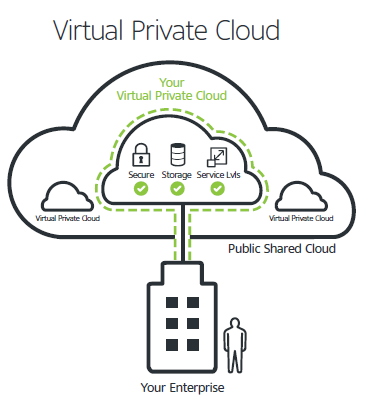
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
The Virtual Private Cloud offers isolated infrastructure and is housed on a public cloud. It’s perfect for businesses who want the protection of a private cloud combined with the flexibility of a public cloud. A well-liked option for pipelines for cloud data engineering.
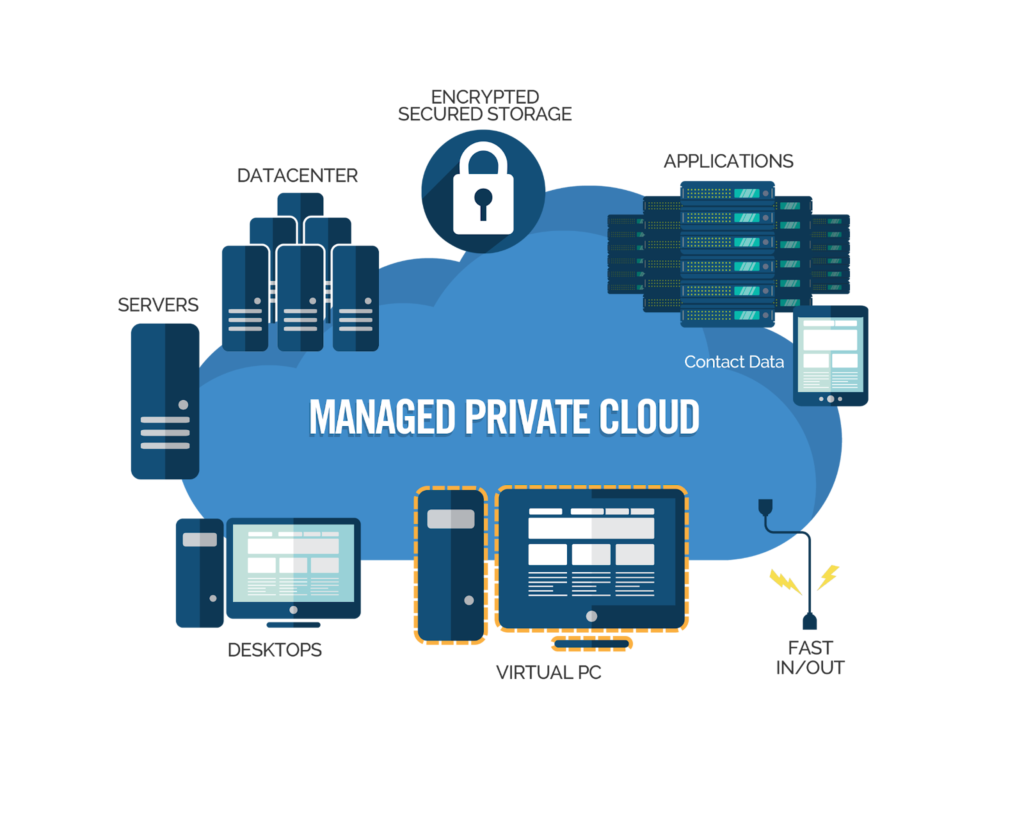
Managed Private Cloud
Managed Private Cloud is completely controlled by third-party service providers such as VMware Cloud on IBM Cloud. The vendors are responsible for supporting, upgrading, and maintaining the managed cloud. Businesses without internal cloud management expertise will find these options appealing. Managed Private Cloud provides reassurance and reliable SLAs – a sweet spot between private and public cloud computing.
Hosted Private Cloud
Hosted Private Clouds are housed in an external data center but are separated for each organization. The purpose of hosted cloud solutions is to give companies a more adaptable, convenient, and economical approach for utilizing the advantages of the cloud. In a hosted private cloud, infrastructure is leased and not shared, reducing management overhead while preserving security.
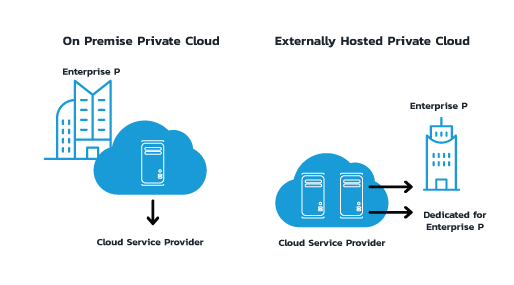
On-Premise Private Cloud
On-premises private cloud is internally implemented and maintained by a company. It offers maximum customization and compliance control at a high initial cost. Sectors like Healthcare and Government prefer on-premises private cloud.
Private Cloud Security
Private cloud architecture excels in security. The private cloud environments’ security is strengthened by:
- Zero Trust Architectures
- AI-based threat intelligence
- Cloud-native firewalls
- End-to-end encryption
Additionally, to ensure strong control, compliance automation tools continuously audit an organization’s cloud architecture against standards like ISO 27001 or SOC 2.
Private Cloud Meets Emerging Technologies
In the age of edge computing, AI, and Web3, private cloud infrastructures are no longer monolithic. Emerging use cases include:
- Edge Private Clouds: Miniaturized cloud environments for real-time processing
- AI Model Training: Training large ML models on secure, GPU-powered nodes
- Containerized Microservices: Private Kubernetes clusters with policy-based scaling
- Cloud Data Engineering Pipelines: Fast, secure ETL/ELT pipelines integrated with Snowflake, Databricks, and BigQuery
Upskill with WeCloudData: Become a Cloud Engineer & Analytics Leader
Want to become a cloud data scientist, cloud engineer, or security architect? At WeCloudData, we help professionals like you break into the tech industry with career-focused Cloud Computing & Data Programs designed by industry experts in Canada. We offer the top-rated DevOps courses in Toronto, Canada
Our Cloud Engineer Track delivers a comprehensive, hands-on approach to cloud engineering, equipping you with the skills to design, deploy, and manage secure, scalable, multi-cloud environments. The courses included in the cloud computing learning track include;
- Python Fundamentals
- Introduction to Linux
- Introduction to Docker
- AWS Fundamentals
- Azure Fundamentals
- GCP Fundamentals
Why This Program?
- End-to-End Cloud Mastery: From core principles to advanced architectures across AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Enterprise-Grade Skills: Learn industry best practices for DevOps, resilience, and cost-optimized solutions.
- Real-World Readiness: Apply knowledge through hands-on projects and case studies mirroring modern IT challenges.
Who Should Enroll?
- Aspiring Cloud Engineers and Architects
- DevOps & SRE Professionals expanding their cloud expertise
- Tech professionals transitioning to multi-cloud environments
Visit WeCloudData to start your journey into Cloud Computing!

