With the advancement in digital technology, organizations are seeking secure, collaborative, and cost-effective cloud solutions. Community cloud computing is a model that perfectly fits these criteria. A community cloud is a cloud computing infrastructure shared among a specific group of organizations that share common interests, objectives, or concerns.
This blog explores the concept of community cloud computing, its uses, especially in government sectors, and its benefits. Let’s learn community clouds with WeCloudData!
What Is Community Cloud
Community clouds offer a middle ground between public clouds, which are accessible to everyone, and private clouds, which are dedicated to a single organization. They enable multiple organizations to share resources while preserving some exclusivity and control. A community cloud is a multi-tenant collaborative infrastructure designed for use by a specific community of users from organizations with shared requirements, including security, compliance, performance, and regulatory aspects. The community can be defined by various factors, including:
- Industry: Financial institutions, healthcare providers, or educational institutions.
- Geography: Organizations within a specific region.
- Goal: Non-profit organizations with similar objectives or research institutions collaborating on a project.
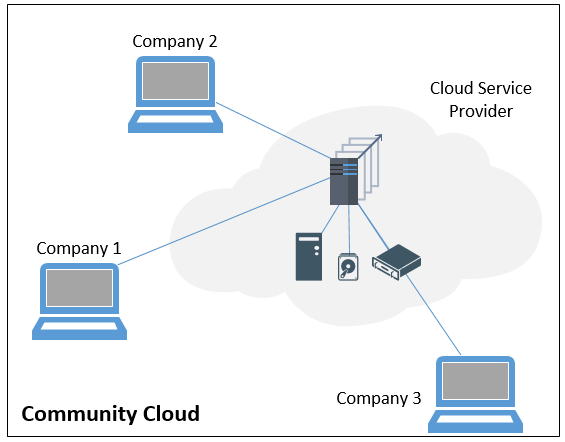
How Community Cloud Works
The principle behind a community cloud is the sharing of infrastructure and resources among a group of organizations that have common needs and goals. A community cloud is designed for collaboration within a specific group, as opposed to a private cloud, which is owned by a single organization, or a public cloud, where resources are shared among a large and diverse user base.
Here’s a breakdown of how community cloud typically works:
- Defined Community: The first rule is to define the common thread that binds the potential users. The community is defined by shared characteristics, such as industry, geography, regulations, and mission.
- Shared Infrastructure: Resources, including hardware, software, and network, are pooled and shared among community members.
- Collaborative Governance: Members often participate in setting policies and managing the cloud.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance: Implements measures relevant to the community’s shared needs, such as HIPAA and GDPR.
- Cost Sharing: Members share expenses, which offers potential savings.
- Focused Services: Provides IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS offerings relevant to the community’s work.
- Managed Access: Secure and isolated environments for each member within the shared infrastructure.
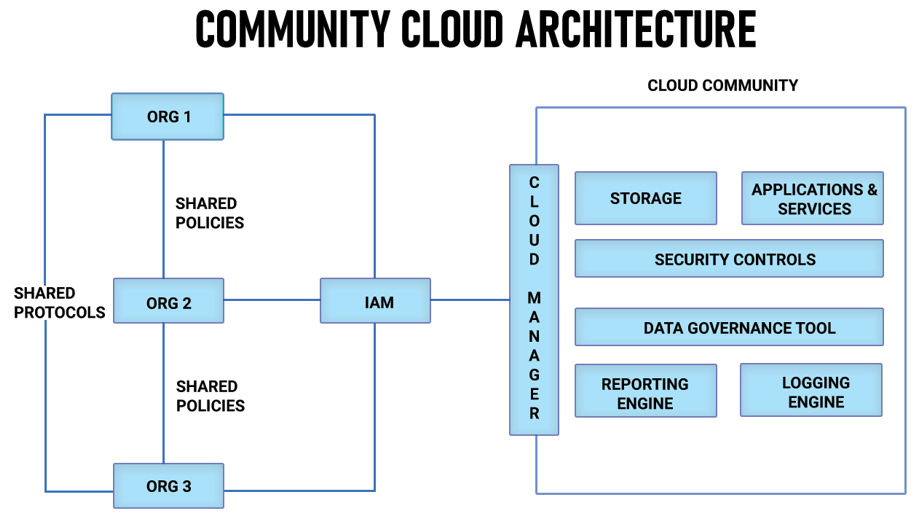
Community Cloud vs. Public, Private, and Hybrid Clouds
It is essential to understand the differences between community clouds and other cloud computing models:
It is essential to understand the differences between community clouds and other models:
Public Cloud: Accessible to every user; economical, but offers reduced data control.
Private Cloud: Tailored for a single organization; provides the highest level of control, but comes with increased expenses.
Hybrid Cloud: Merges public and private clouds; offers flexibility but can be challenging to manage.
Community Cloud: A shared resource for organizations with aligned objectives, seeks to balance cost, control, and collaboration.
Every model caters to distinct needs, and the selection is based on considerations such as budget, security needs, and collaboration objectives.
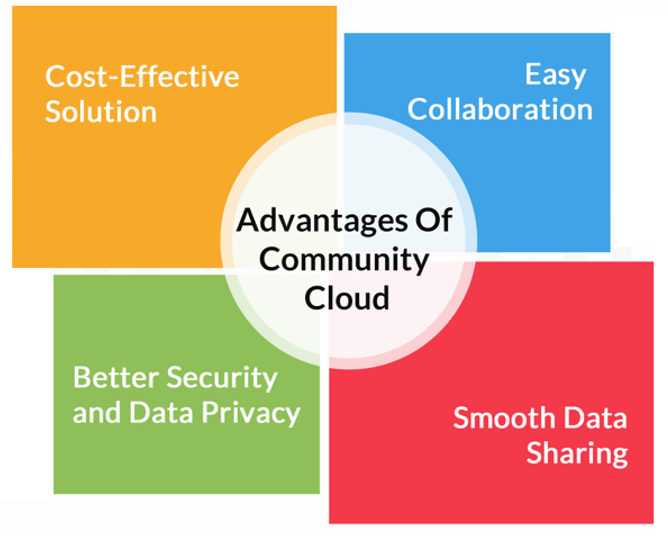
Benefits of Community Cloud
Community cloud offers multiple benefits. The advantages of opting for community cloud are listed below;
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Access to platforms and services personalized to the unique workflows and challenges of the target industry.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Enables smooth data exchange and teamwork with other reliable organizations in the community.
- Cost-effectiveness: Utilizing shared resources can lead to reduced operational and capital costs compared to individual private clouds.
- Accelerated Adoption of Best Practices: The transmission of knowledge and best practices among community members can speed up the adoption of effective cloud strategies.
- Compliance and Security: Organizations can customize community clouds to meet specific regulatory requirements. This ensures that all members meet the required standards.
Community Cloud Examples
Government Community Cloud (GCC)
The Government Community Cloud (GCC) is a secure cloud setting designed specifically for government agencies at the federal, state, and local levels in the U.S. Services like Microsoft’s GCC provide advanced security features to comply with strict government standards, promoting inter-agency collaboration while safeguarding data.
Educational Institutions
Enabling collaboration and resource sharing among universities, colleges, and schools. Using a community cloud model lowers costs and promotes innovation among all involved schools and universities.
Financial Services Community Clouds
Designed for banks, insurance firms, and investment companies that have strict security and compliance needs, such as PCI DSS and GDPR.
Community Cloud – The Backbone of Secure, Collaborative Digital Ecosystems
Community cloud computing offers a strategic option for organizations seeking collaborative, secure, and budget-friendly cloud solutions. By understanding its benefits and applications and by pursuing relevant training opportunities, professionals and organizations can position themselves at the forefront of cloud innovation.
Learn with WeCloudData: Upskill Your Team in Cloud & Data Technologies
Looking to empower your team with the latest in cloud computing, data engineering, and AI technologies? WeCloudData’s Corporate Training tailors its programs to meet the needs of forward-thinking companies. With hands-on, expert-led instruction, our courses design aims to bridge the skills gap and help your organization thrive in today’s data-driven economy.
Upskill with WeCloudData: Become a Cloud Engineer & Analytics Leader
Our Cloud Engineer Track delivers a comprehensive, hands-on approach to cloud engineering, equipping you with the skills to design, deploy, and manage secure, scalable, multi-cloud environments. The courses included in the cloud computing learning track include;
- Python Fundamentals
- Introduction to Linux
- Introduction to Docker
- AWS Fundamentals
- Azure Fundamentals
- GCP Fundamentals
Why This Program?
- End-to-End Cloud Mastery: From core principles to advanced architectures across AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Enterprise-Grade Skills: Learn industry best practices for DevOps, resilience, and cost-optimized solutions.
- Real-World Readiness: Apply knowledge through hands-on projects and case studies mirroring modern IT challenges.

