Healthcare is one of the industries most heavily influenced by digital transformation. Technology has reshaped how care is delivered, managed, and optimized. Cloud computing in the healthcare industry is one of the most promising technologies that has potential to make remarkable changes.
In this blog, we’ll explore how cloud computing is shaping the medical domain. Let’s learn more with WeCloudData!
Cloud Computing in Healthcare
In healthcare, cloud computing refers to the use of scalable and secure cloud infrastructure for flexible and secure data management. Cloud computing in the healthcare industry facilitates the efficiency by eliminating the need for expensive, inflexible IT infrastructure, while promoting agility, innovation, and improved patient care.
Healthcare sector spending on cloud computing is expected to reach a global market value of over $89 billion by 2027, driven by the rapid growth of this technology. Additionally, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), a common cloud model for migrating healthcare infrastructure to the cloud, is now the fastest-growing cloud service, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32% by 2027.
There are three major cloud services used in the healthcare industry:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Offers virtualized computing resources, such as servers and storage.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Provides platforms for developing and managing healthcare apps.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): EHRs (Electronic Health Records) and other cloud-based apps that simplify administrative and clinical tasks.
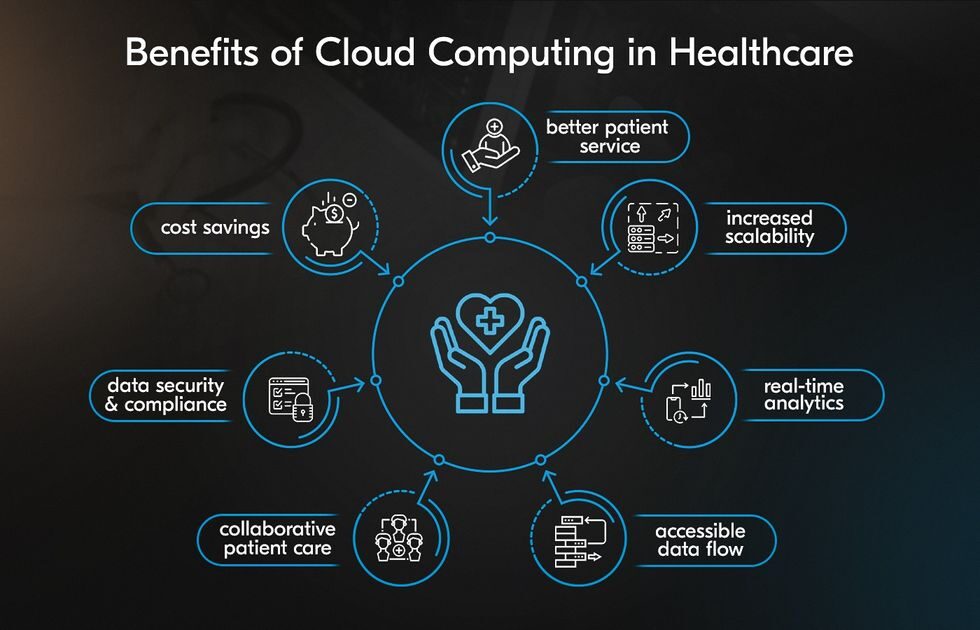
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
The use of cloud computing in the healthcare industry offers numerous advantages to healthcare providers. Better patient outcomes, increased teamwork, and cost savings are the three main categories into which these advantages can be divided. Each of these areas offers benefits that have the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare organizations operate and deliver treatment.
Improved Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud platforms provide real-time access to medical records, test results, and treatment plans. Doctors have quick access to patient data, regardless of whether they work in a multi-site hospital or a rural clinic.
- Cloud-powered telemedicine technologies let physicians consult with patients from a distance without compromising the quality of the data.
- MRI scans submitted by a radiologist in one location can be viewed by a cardiologist anywhere in the world.
Scalability and Cost Efficiency
Cloud computing allows healthcare organizations to pay only for the resources they use. This cloud model enables organizations to scale services up or down based on their demand. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many hospitals moved to the cloud to scale up remote patient monitoring tools and telehealth consultations.
Enhanced Data Security and Compliance
Cloud computing providers offer robust security protocols. HIPAA-compliant cloud solutions utilise access control, encryption, and regular audits to protect patient data. Cloud providers also provide disaster recovery and backup solutions, minimizing the risk of data loss.
Faster Innovation and AI Integration
Cloud infrastructure supports rapid testing and deployment of AI and machine learning models. Whether it’s predicting patient deterioration or automating administrative tasks, cloud-powered AI accelerates healthcare innovation.
Centralized Patient Records and Big Data Analytics
Cloud computing supports centralized data repositories that can analyze both structured and unstructured health data for improved clinical and operational insights. For instance:
- Predictive analytics can help detect disease outbreaks.
- Real-time monitoring dashboards help hospitals manage bed capacity.
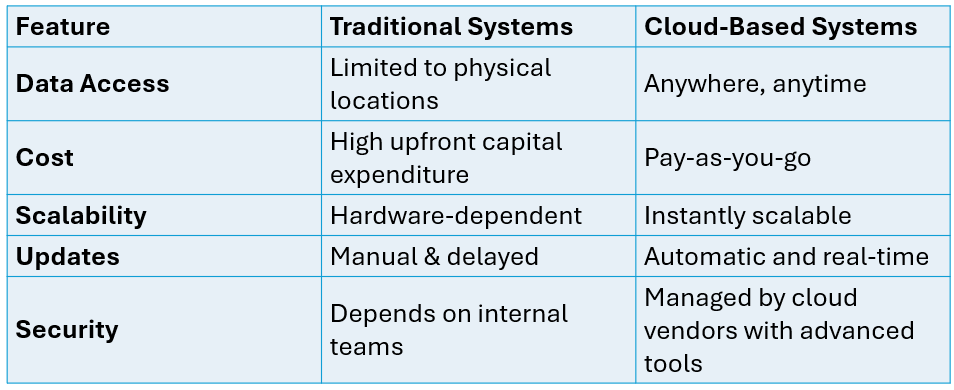
Advantages of Cloud Computing in Healthcare over Traditional Systems
The advantages of cloud computing in healthcare become clear when compared with legacy systems:
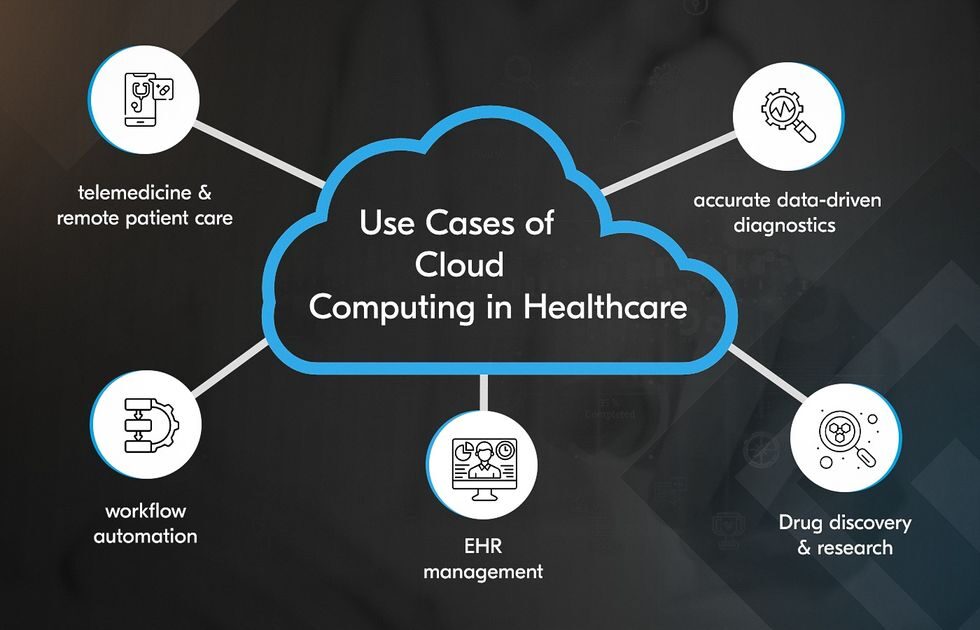
Real-World Use Cases of Cloud Computing and Healthcare
Cloud computing is rapidly adopted in healthcare due to the transformative results it brings to patient care and diagnostics. Some key areas where this effect is dominated are briefly explained below;
Mayo Clinic (USA)
The Mayo Clinic and Google Cloud announced a 10-year strategic partnership to support its digital transformation. This partnership will redefine how healthcare is delivered and accelerate the pace of innovation in healthcare through digital technologies. Mayo will utilize advanced cloud computing, data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) to redefine healthcare delivery, bringing together global providers and consumers to improve healthcare.
NHS (UK)
The UK’s National Health Service is exploring and implementing the use of cloud platforms to store and analyze data from wearable devices for managing chronic conditions such as heart disease and diabetes.
Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System implemented a cloud-native electronic health record (EHR) system, which allowed them to improve clinical documentation, streamline workflows, and enhance the patient experience.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the potential of cloud computing in healthcare, there are many challenges and considerations to consider.
Compliance and Data Privacy
Cloud providers are subject to strict regulations, including the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Healthcare providers need to perform due diligence to ensure compliance.
Complexity of Data Migration
Migrating to the cloud from a legacy healthcare system can be expensive and technically complex. However, a well-planned migration strategy mitigates risks and enhances ROI.
Downtime and Connectivity
Mission-critical healthcare systems must have reliable connectivity and uptime, as cloud systems rely on internet access.
Why Cloud Computing Is the Backbone of Digital Health
As society grows increasingly dependent on digital solutions, cloud computing plays a vital role in transforming healthcare. The real-world applications of cloud technology, including telemedicine, electronic health record (EHR) management, and data-driven diagnostics, demonstrate its transformative potential. Cloud computing offers a flexible, secure, and intelligent infrastructure that supports everything from patient engagement to drug discovery. A healthcare organization using cloud computing enjoys;
- Data-driven decision-making
- Better patient experiences
- Operational agility
- Lower costs
Whether it’s improving collaboration, reducing costs, or supporting AI innovation, the advantages of cloud computing in healthcare are undeniable. Healthcare organizations that strive to stay competitive and patient-centered are building tomorrow’s care on the foundation of the cloud.
Upskill with WeCloudData: Become a Cloud Engineer & Analytics Leader
Looking to empower your team with the latest in cloud computing, data engineering, and AI technologies in Canada? Our Cloud Engineer Track delivers a comprehensive, hands-on approach to cloud engineering, equipping you with the skills to design, deploy, and manage secure, scalable, multi-cloud environments. The courses included in the cloud computing learning track include;
- Python Fundamentals
- Introduction to Linux
- Introduction to Docker
- AWS Fundamentals
- Azure Fundamentals
- GCP Fundamentals
What WeCloudData Offers
- Live public training sessions led by industry experts
- Career workshops to prepare you for the job market
- Dedicated career services
- Portfolio support to help showcase your skills to potential employers.
- WeCloudData’s Corporate Training tailors its programs to meet the needs of forward-thinking companies. With hands-on, expert-led instruction, our courses designs to bridge the skills gap and help your organization thrive in today’s data-driven economy.
Join WeCloudData to kickstart your learning journey and unlock new career opportunities in Artificial Intelligence.

